Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction To BIOS :
BIOS, or Basic Input/Output System, is a important firmware program stored on a chip embedded in your computer’s motherboard. This program comes pre-installed by the motherboard’s manufacturer and resides within an Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM) chip. Within this chip, a set of instructions takes the form of a program. When you ‘power-on‘ your computer, the microprocessor hands over control to the BIOS program, which always resides in this chip.
It’s important to note that Random Access Memory (RAM) is faster than Read-Only Memory (ROM). In modern computers, to Speed up the boot process, BIOS instructions are copied from ROM to RAM. This process of moving BIOS instructions from ROM to RAM is known as ‘Shadowing‘ or ‘Shadow/Shadowing.’ This enables quicker access to the essential instructions during the startup process.”
Today, we have Flash BIOS, which enables users to update the BIOS program as necessary. Flash BIOS, a modern advancement, empowers users to keep their BIOS programs up-to-date with ease.
This technology allows for convenient and hassle-free updates, ensuring that your computer’s firmware remains compatible with the latest hardware and software developments. It’s a user-friendly way to enhance system functionality and security. Say bye-bye to the complexities of traditional BIOS updates, thanks to Flash BIOS.

The BIOS Startup Process :
The BIOS Startup Process includes POST, Hardware Checks, and Error Diagnostics. let’s discuss them one by one.
When the computer is powered on , the microprocessor starts by trying to perform BIOS commands or say instructions. These instructions serve the important role of loading the operating system, which resides on the hard disk, through the BIOS’s bootstrap program.
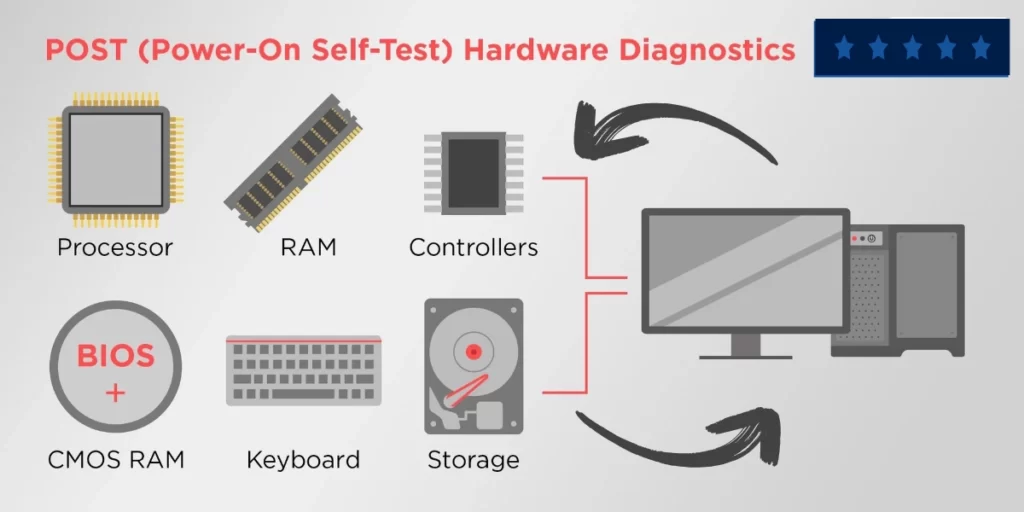
Simultaneously, the BIOS initiates the ‘Power On Self Test‘ (POST) process, a fundamental procedure in the computer’s journey to life.
The main job of POST is to carefully check all the computer’s hardware components. This includes scrutiny of input/output devices, serial/parallel ports, and various internal elements. POST methodically sends signals to these components, ensuring that each one is functioning impeccably in its designated role.
This comprehensive hardware check is the BIOS’s way of certifying that every piece of the system is ready for action.
However, the watchful POST process doesn’t end its work here. If, during its examination, it detects any anomalies or issues with a hardware component, it takes decisive action.
This could involve halting the loading of the operating system to prevent further complications. POST acts as a diagnostic guardian for your system, standing guard against potential hardware-related hiccups.
For instance, during the POST process, if your computer produces distinctive beeping sounds, it’s akin to the BIOS’s way of signaling a red flag. This auditory language translates to a hardware issue.
Remarkably, different beep codes exist, each with a specific meaning, facilitating the precise diagnosis of the problem. Whether it’s a minor glitch or a more serious hardware concern, these beep codes are the BIOS’s mode of communication in a world where silence could be costly.
Common Beep Codes meanings during the POST Process :
- No Beep: This typically indicates a power supply or motherboard issue.
- One Short Beep: It usually signifies that the computer is booting up normally.
- One Long Beep, Two Short Beeps: This code often points to a video card or display-related problem.
- Continuous Beeping: This may indicate a RAM (memory) problem or other hardware issues.
- Two Short Beeps: It might suggest a CMOS (BIOS settings) issue.
- Three Short Beeps: This code can indicate a keyboard-related problem.
- Four Short Beeps: It may signify a problem with the system timer.
- Five Short Beeps: It is often associated with a CPU (processor) error.
- Six Short Beeps: This beep code can point to a keyboard controller error.

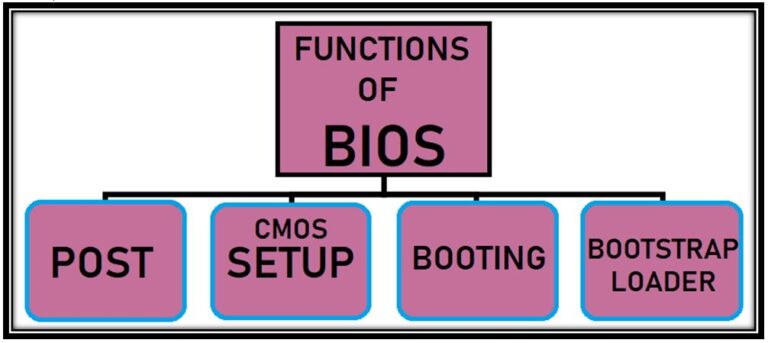
Key Functions of BIOS:
1. Power-On Self-Test (POST): When you switch on your computer, BIOS runs a series of checks known as POST. It examines the hardware components like the processor, memory, and storage devices to ensure they’re functioning correctly. If any issue is detected, BIOS may alert you with beeps or error messages.
2. Booting the Operating System: BIOS is responsible for initiating the boot process. It searches for the operating system (like Windows or macOS) and loads it into the computer’s memory (RAM). This kickstarts your computer and allows you to interact with the OS.
3. CMOS Setup: BIOS stores essential hardware settings, such as the system clock and boot sequence, in a special memory called CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor). You can access and modify these settings through the CMOS setup utility, which is often referred to as BIOS setup. This allows you to customize your computer’s behavior.
4. Bootstrap Loader: BIOS includes a bootstrap loader that locates the operating system. It serves as the initial guide in finding and starting the OS.
5. Software/Drivers: BIOS is responsible for locating the necessary software and drivers that interface with the operating system once it’s running. These software and drivers enable hardware components to function correctly within the OS environment.
6. BIOS Updates: BIOS can be updated to provide compatibility with new hardware, fix bugs, or enhance security. Manufacturers release BIOS updates from time to time, and users can install them to improve their computer’s performance and functionality.
These six functions make BIOS an indispensable component of your computer’s operation, ensuring proper hardware initialization, seamless booting, user customization, and the effective functioning of software and drivers.
Uses of BIOS (Basic Input Output System):
The primary function of BIOS (Basic Input Output System) is to serve as a important intermediary between operating systems (OS) and the hardware they operate on. This role is crucial, as BIOS effectively bridges the gap between the microprocessor and the control of input/output (I/O) devices, ensuring a smooth flow of information and data.
While BIOS generally facilitates this communication, it possesses the capacity to enable direct data transfer from specific devices like video cards to memory. This capability significantly enhances data transfer speeds, optimizing the overall performance of the computer system.
Basically, BIOS functions as mediator, facilitating the smooth interaction between the computer’s software and hardware components. Its role is fundamental from the moment a user powers-on their computer, allowing for seamless functionality and efficient data management.
Throughout the history of computing, BIOS has remained an indispensable component, adapting and evolving in tandem with technological advancements. BIOS, or Basic Input Output System, plays a pivotal role in computer functionality. It serves as a bridge between hardware and software, ensuring smooth communication. Here are some of the versatile uses of BIOS:
Hardware Initialization: BIOS initializes critical hardware components of your system, when you power-on your computer, ensuring they’re ready for operation.
Bootstrapping: It’s responsible for loading the operating system from your storage devices, It’s responsible for initiating the boot process of your computer, getting your system up and running computer’s functionality.
System Checks: BIOS conducts the Power On Self Test (POST), verifying hardware integrity and signaling any issues during startup.
Customization: Computer users can access BIOS settings to customize hardware configurations, such as setting boot priorities or enabling virtualization, etc.
Security: BIOS can include security features like passwords to protect your system from unauthorized access.
Legacy Support: In older systems, BIOS helps maintain compatibility with legacy software and hardware.
Overclocking: Enthusiasts use BIOS to tweak CPU and memory settings for performance optimization.
Updating Firmware: BIOS updates can be applied to enhance compatibility, add features, and bolster security.
Diagnostic Tools: Some BIOS versions offer diagnostic utilities to troubleshoot hardware issues.
Legacy OS Support: BIOS can provide support for older operating systems that rely on specific BIOS functions. Basically, BIOS is the silent conductor orchestrating your computer’s symphony, ensuring everything functions harmoniously from the moment you hit the power button.
How Does BIOS Function?
BIOS, or Basic Input Output System, can be likened to your computer’s brain. It’s always ready, ever-present, residing on a chip embedded in the motherboard. While it lacks the complexity of software like Windows, BIOS plays a fundamental role in your computer’s operation or functionality.
At first when you press the power button, your computer’s microprocessor, its ‘computer’s tiny brain,’ awakens and promptly hands over control to BIOS, which resides on a special chip known as EPROM.
After that BIOS begins with a quick checkup, ensuring all essential components are connected and functioning correctly. These components are like the computer’s assistants, holding the necessary files to start the system, referred to as ‘Boot Devices.’
Once BIOS gives the green light to these boot devices, it proceeds to wake up the operating system, like Windows, stored on your computer’s hard drive. Imagine this process as a ‘wake-up call’ to your computer. BIOS gives it a little prompt, and your computer awakens and springs into action.
How To Enter BIOS Settings (Accessing and Modifying BIOS)
Whenever you need to adjust hardware settings, the ‘BIOS Setting’ is the place to go. Fortunately, it’s not too complicated to access and change BIOS settings using the BIOS Setup Utility. Here’s how you can enter into BIOS and you can access and modify BIOS settings:
1. Power Off or Restart:
Start by turning off your computer or giving it a quick restart.
2. Keep an Eye Out:
As your computer starts up, watch for a message like “Entering Setup” or something similar. It will also specify which key to press to enter the setup. You might see something like “Press [key] to enter BIOS setup.” The keys they mention are usually Esc, Del, Tab, or one of the function keys (F1 To F12).
3. Quickly Press the Key:
As soon as you see that message, press the indicated key. Timing is key here.
4. Inside the BIOS Setup Utility:
You’re now in the BIOS Setup Utility. This is your control center for making various changes, such as tweaking hardware, adjusting memory settings, changing the boot order, or even resetting your BIOS password. It’s where you customize your computer’s performance to suit your preferences.

BIOS Manufacturers and Their Impact :
Let’s talk about BIOS manufacturers and their history. Initially, BIOS was the product of IBM, but innovative minds like those at Phoenix Technologies saw an opportunity. They crafted their BIOS, drawing inspiration from IBM’s creation.
This step opened way for producing IBM-compatible PCs and even computers not originating from IBM yet smoothly functioning with BIOS. Among the pioneers in this world was Compaq.
The Evolution of BIOS: The term “BIOS” was originally coined in 1975 by ‘Gary Kildall‘, an American computer scientist. It found its way into IBM’s inaugural personal computer in 1981, marking a significant milestone in computing history. As technology progressed, BIOS underwent a series of modifications, with the transition from Read-Only Memory (ROM) to Flash BIOS simplifying updates and adaptability.
However, BIOS’s reign began to face a formidable challenger: Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). UEFI brought a slew of modern enhancements, including graphical interfaces and accelerated boot times. In 2017, Intel announced its intentions to retire support for legacy BIOS systems by 2020, signifying a pivotal shift towards UEFI’s widespread adoption.
Today, while UEFI has taken the lead, reflecting on the history of BIOS reminds us of its indelible contribution to the formative years of personal computing.
In modern times, numerous companies incorporate BIOS chips into the motherboards they manufacture. Here are some prominent examples:
- AMI (American Megatrends)
- Asus
- Dell
- IBM
- Intel
- ECS (Elitegroup Computer Systems)
- Foxconn
- Hewlett Packard (HP)
Understanding the manufacturer of your motherboard holds importance, particularly when you consider BIOS and chipset driver updates.
These updates play a crucial role in enabling your computer’s operating system to communicate effectively with components like your video card.
Keeping them up to date enhances your computer’s performance and addresses potential security concerns. It’s worth noting that each company has its unique approach to updating these drivers, so the process may vary depending on your motherboard’s manufacturer.
BIOS FAQs: Answering Your Basic Input/Output System Questions
What is a BIOS?
BIOS, or Basic Input/Output System, is firmware that boots up your computer. It’s a fundamental component that initializes hardware components, ensuring your computer runs smoothly.
What is a BIOS used for?
BIOS is used to initialize and test hardware during the computer’s startup process. It also loads the operating system and allows users to configure system settings.
What is BIOS full form?
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System.
What is BIOS and its types?
BIOS is firmware that loads when you start your computer. Types include traditional BIOS and UEFI, each with different functions and features.
Why is BIOS called BIOS?
BIOS is called so because it handles the basic input and output operations for a computer’s hardware components.
How BIOS Work?
BIOS works by conducting self-tests on computer hardware, initializing devices, and loading the operating system. It also manages system settings.
How to Update BIOS?
BIOS updates can usually be obtained from your motherboard manufacturer’s website. Follow their instructions for a safe update.
How to enter the BIOS on Windows 11 or 10?
To enter the BIOS on Windows 11 or 10, restart your computer, press the designated key (often Del, F2, or F12), and access the BIOS setup.
What Is the Purpose of BIOS for a Computer?
The purpose of BIOS is to initialize hardware, boot the operating system, and provide configuration options to users.
BIOS Full Form:
The full form of BIOS is Basic Input/Output System, that manages hardware initialization and communication.
UEFI vs BIOS: What’s the Difference?
UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is a modern replacement for BIOS. It offers advanced features, including a secure boot, and a more user-friendly interface.
What is PS2 bios?
The PS2 BIOS is firmware for Sony’s PlayStation 2 gaming console, essential for running PS2 games on an emulator.
What is psx bios?
The PSX BIOS is firmware for Sony’s original PlayStation gaming console, required for running PSX games on an emulator.
How to update BIOS?
To update BIOS, visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website, download the latest BIOS version, and follow their instructions for updating.
Dell BIOS update
Dell provides BIOS updates for their computers to improve performance, security, and compatibility. You can find these updates on the Dell website.
HP BIOS update
HP offers BIOS updates for their computers. Visit HP’s official website and download the necessary updates for improved system performance.
How to enter BIOS?
To enter BIOS, restart your computer, and press the appropriate key (commonly Del, F2, or F12) during startup. This allows you to access BIOS settings.
How to get into BIOS?
To access BIOS, restart your computer and press the designated key during startup. It allows you to enter the BIOS setup.
How to enter BIOS Windows 10?
To access BIOS on Windows 10, restart your computer and press the relevant key during startup, usually Del or F2.
How to open BIOS?
To open BIOS, restart your computer and press the required key to access BIOS settings during the startup process.
How to get to BIOS?
To get to BIOS, restart your computer and press the specified key (such as Del, F2, or F12) to enter the BIOS setup.
What is BIOS in a computer?
BIOS in a computer is firmware responsible for hardware initialization, the boot process, and providing configuration options to users.
What is BIOS update?
A BIOS update is new firmware released by a motherboard manufacturer to improve compatibility, fix issues, and enhance security.
What is BIOS flashback?
BIOS flashback is a feature that allows you to update your BIOS even if your system doesn’t boot. It helps recover from failed BIOS updates.
What is BIOS updates?
BIOS updates refer to new firmware versions provided by motherboard manufacturers to enhance performance and address security concerns.
What is BIOS setup?
BIOS setup is the configuration interface where you can adjust hardware settings and system parameters.
What is XMP in BIOS?
XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) in BIOS is a feature used to overclock RAM modules to achieve higher memory speeds.
What is a BIOS update?
A BIOS update is new firmware provided by motherboard manufacturers to enhance system stability, compatibility, and performance.
What is CSM in BIOS?
CSM, or Compatibility Support Module, in BIOS, allows older software and operating systems that rely on legacy BIOS functions to run on newer UEFI-based systems.
What is BIOS password?
A BIOS password is a security feature that prevents unauthorized access to BIOS settings and system startup. It’s set by users to protect their computers from tampering.
MSI BIOS?
MSI BIOS refers to the firmware used in MSI motherboards. MSI provides BIOS updates and customization options for their motherboards.
Asus BIOS?
Asus BIOS is the firmware used in Asus motherboards. Asus offers BIOS updates and various settings to optimize system performance.
Como entrar en la BIOS (How to enter the BIOS)?
Para entrar en la BIOS, reinicia tu ordenador y presiona la tecla designada durante el proceso de arranque. Esto te permitirá acceder a la configuración de la BIOS.
PCSX2 BIOS?
PCSX2 BIOS refers to the BIOS needed for running PlayStation 2 games on the PCSX2 emulator.
How to reflash BIOS?
Reflashing BIOS means updating or reinstalling BIOS firmware on your motherboard. To do this, follow your motherboard manufacturer’s instructions.
Error BIOS/Legacy boot or UEFI-only media?
This error occurs when there’s a compatibility issue between the BIOS/legacy boot mode and UEFI-only bootable media. It can be resolved by adjusting your boot settings.
Lenovo BIOS
Lenovo BIOS is the firmware used in Lenovo computers. Lenovo provides BIOS updates and customization options for their devices.
Lenovo BIOS key
The key to access Lenovo BIOS settings varies but is commonly F1, F2, or F12 during startup.
BIOS meaning
BIOS, short for Basic Input/Output System, refers to the firmware responsible for initializing hardware and managing essential computer functions.
HP BIOS key
The key to access HP BIOS settings is typically Esc, F10, or F12, depending on the HP computer model.
